Binomial Queue is a #Priority Queue/Heap that seeks to improve Leftist Heap’s and Skew Heap’s Insert. Unlike those, it is a collection of Linked List Tree.
Illustration
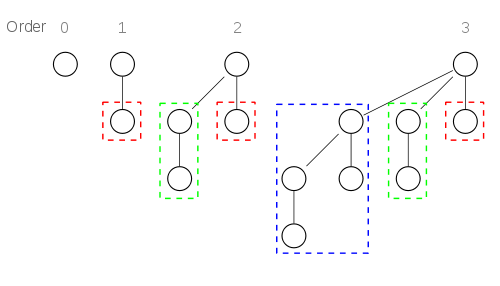
Analysis
- Insert will result in \(O(1)\).
- Merge and DeleteMin will result in \(O(\log N)\).
- FindMin could result in \(O(\log N)\) if the minimum is not known
Implementation
#ifndef _BinomialQueue_H
struct BinNode;
struct Collection;
typedef struct BinNode *Position;
typedef struct Collection *BinQueue;
BinQueue Initialise(void);
int IsEmpty(BinQueue H);
ElementType FindMin(BinQueue H);
BinTree CombineTrees(BinTree T1, BinTree T2);
BinQueue Merge(BinQueue H1, BinQueue H2);
ElementType DeleteMin(BinQueue H);
#endifstruct BinNode {
ElementType Element;
Position LeftChild;
Position NextSibling;
};
/**
* Return the result of merging equal-sized T1 and T2
*/
BinTree CombineTrees(BinTree T1, BinTree T2) {
if (T1->Element > T2->Element)
return CombineTrees(T2, T1);
T2->NextSibling = T1->LeftChild;
T1->LeftChild = T2;
return T1;
}
/**
* Merge two binomial queues
* Not optimised for early termination
* H1 contains merged result
*/
BinQueue Merge(BinQueue H1, BinQueue H2) {
BinTree T1, T2, Carry = NULL;
if (H1->CurrentSize + H2->CurrentSize > Capacity)
Error("Merge would exceed capacity");
H1->CurrentSize += H2->CurrentSize;
for (int i = 0, j = 1; j <= H1->CurrentSize; i++, j *= 2) {
T1 = H1->TheTrees[i];
T2 = H2->TheTrees[i];
switch (!!T1 + 2*!!T2 + 4*!!Carry) {
case 0: // No trees
case 1: // Only H1
break;
case 2: // Only H2
H1->TheTrees[i] = T2;
H2->TheTrees[i] = NULL;
break;
case 4: // Only Carry
H1->TheTrees[i] = Carry;
Carry = NULL;
break;
case 3: // H1 and H2
Carry = CombineTrees(T1, T2);
H1->TheTrees[i] = H2->TheTrees[i] = NULL;
break;
case 5: // H1 and Carry
Carry = CombineTrees(T1, Carry);
H1->TheTrees[i] = NULL;
break;
case 6: // H2 and Carry
Carry = CombineTrees(T2, Carry);
H2->TheTrees[i] = NULL;
break;
case 7: // All Trees
H1->TheTrees[i] = Carry;
Carry = CombineTrees(T1, T2);
H2->TheTrees[i] = NULL:
break;
}
}
return H1;
}
ElementType DeleteMin(BinQueue H) {
int MinTree; // The tree with the minimum item
BinQueue DeletedQueue;
Position DeletedTree, OldRoot;
ElementType MinItem;
if (IsEmpty(H)) {
Error("Empty binomial queue");
return -Infinity;
}
MinItem = Infinity;
for (int i = 0; i < MaxTrees; i++) {
if (H->TheTrees[i] && H->TheTrees[i]->Element < MinItem) {
// Update minimum
MinItem = H->TheTrees[i]->Element;
MinTree = i;
}
}
DeletedTree = H->TheTrees[MinTree];
OldRoot = DeletedTree;
DeletedTree = DeletedTree->LeftChild;
free(OldRoot);
DeletedQueue = Initialise();
DeletedQueue->CurrentSize = (1 << MinTree) - 1;
for (int j = MinTree - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
DeletedQueue->TheTrees[j] = DeletedTree;
DeletedTree = DeletedTree->NextSibling;
DeletedQueue->TheTrees[j]->NextSibling = NULL;
}
H->TheTrees[MinTree] = NULL;
H->CurrentSize -= DeletedQueue->CurrentSize + 1;
Merge(H, DeletedQueue);
return MinItem;
}